umbilical cord blood
What is cord blood?
Cord blood is the blood remaining in the umbilical cord and placenta after a baby is born, which is rich in hematopoietic stem cells. It is usually collected by doctors or midwives and then sent to a cord blood bank by a blood collector.
 Image source: Sichuan Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cell Bank
Image source: Sichuan Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cell BankWhat is cord blood used for?
The "Management Standards for Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Technology (2017 Edition)" issued by the National Health Commission states that hematopoietic stem cells are currently the only stem cells in China that can be used clinically and can only be obtained from bone marrow, peripheral blood, and cord blood.
Cord blood hematopoietic stem cells can treat the following diseases:
- Some malignant hematological diseases: Acute leukemia, chronic leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, and other certain malignancies. Non-malignant diseases: aplastic anemia, severe radiation sickness, severe thalassemia, etc.
- Some genetic, congenital, and metabolic diseases: Typically, after a baby is born, the umbilical cord, placenta, and cord blood are discarded as medical waste. However, there are currently seven cord blood hematopoietic stem cell banks in China, located in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Guangdong, Sichuan, Shandong, and Zhejiang. Local mothers can choose to preserve cord blood.
How to preserve cord blood?
There are two ways to preserve cord blood: donate it for free to a public cord blood bank or pay to store it in a private bank. It is recommended that mothers donate cord blood to their local public cord blood bank rather than spend a large amount of money on private storage.
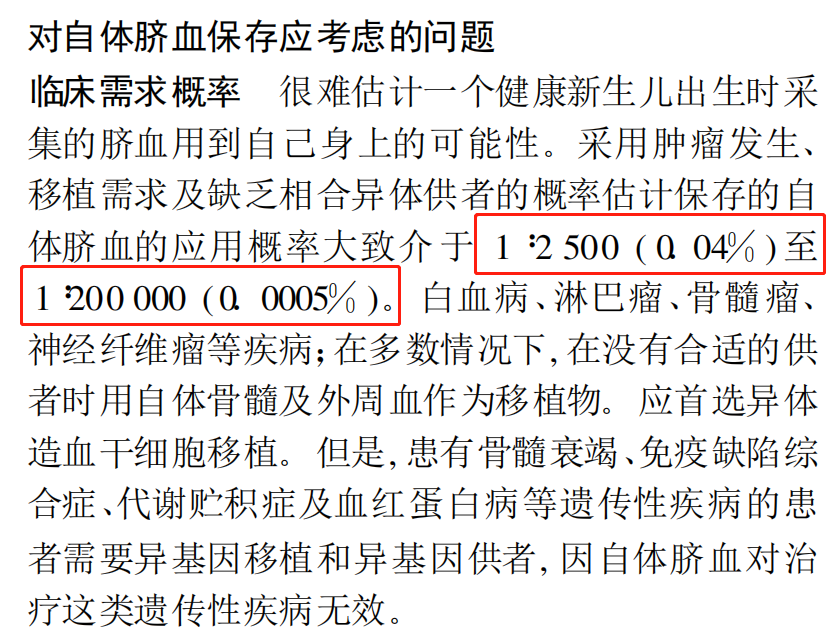
Donating cord blood is recommended. The American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (ASBMT) provided data showing that the probability of a child using their own cord blood is between 0.0005% and 0.04%, which is extremely low.
It’s important to note that if a disease is caused by genetic abnormalities, the stem cells themselves are already problematic, making stored cord blood useless.
For example, if a child develops leukemia, even if the parents have stored the cord blood, it would be of no use, and they would still need to find other matching healthy cord blood. Additionally, the number of stem cells in cord blood is very limited and may not be sufficient to cure certain diseases.
Considering the high cost of private cord blood storage—tens of thousands of yuan, with costs increasing over time (though prices vary slightly by region)—the cost-effectiveness is very low, and it is not recommended for mothers.
Donating cord blood is more meaningful than private storage.
Donating cord blood to a public bank comes with no downsides.
If the baby’s cord blood meets donation requirements, donating it to a public bank ensures priority matching if the child ever needs it in the future.
If more parents choose to donate cord blood, public banks will grow, making it easier to find matches for children who genuinely need them. This significantly improves the efficiency of cord blood use and helps more people in need.
What are the requirements for donating cord blood?
Currently, there are seven cord blood hematopoietic stem cell banks in China, located in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Guangdong, Sichuan, Shandong, and Zhejiang. Following the "one province, one bank" principle, cross-province collection is not allowed.
Donation requirements vary by region, so consult local cord blood bank staff for details.
Before collection:
Below are the cord blood donation screening criteria (pre-collection) in Zhejiang Province for reference:
- The mother is over 18 years old;
- Gestational age is over 34 weeks;
- All prenatal test indicators are normal, including five items: cytomegalovirus (CMV), HIV, syphilis (TP), hepatitis B (HBV), and hepatitis C (HCV);
- No hemoglobinopathies (e.g., thalassemia, G-6-PD deficiency) in the baby’s parents.
After collection:
After collection, medical staff send the cord blood to the bank for further testing, such as:
- Hematopoietic stem cell count (CD34+) and CFU-GM colony levels meet clinical treatment needs;
- Negative for bacterial and fungal cultures;
- Maternal blood pathogen tests meet blood bank standards (non-reactive);
- Normal hemoglobinopathy test results (e.g., thalassemia, G-6-PD deficiency);
- Complete maternal and infant health follow-up records with normal results.
Only if all tests meet requirements will the cord blood be officially stored.